Book an Appointment
KUB Ultrasounds
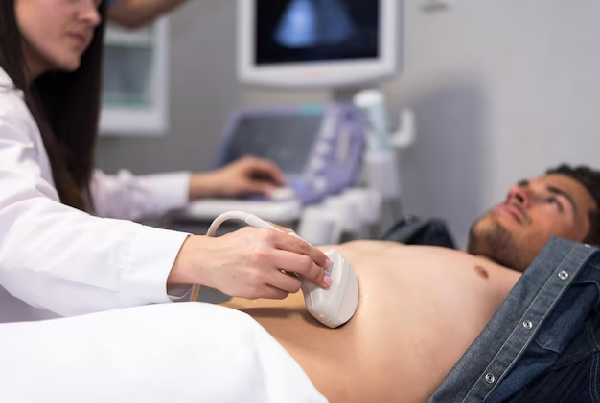
KUB Ultrasounds
A KUB ultrasound, also known as a Kidneys, Ureters, and Bladder ultrasound, is a medical imaging procedure used to assess and visualize the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. It is a non-invasive and painless diagnostic test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the urinary system. Here are key points about a KUB ultrasound:
-
Purpose:
- The primary purpose of a KUB ultrasound is to evaluate the structure, size, and location of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
-
Indications:
- KUB ultrasounds are commonly performed to investigate various urinary system issues, such as kidney stones, urinary tract infections (UTIs), cysts, tumors, and other abnormalities.
-
Procedure:
- The patient typically lies on their back, and a water-based gel is applied to the skin over the abdomen.
- A transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves, is moved over the abdomen to create images of the internal structures.
-
Kidneys:
- The ultrasound can assess the size, shape, and position of the kidneys. It can help identify abnormalities like cysts or tumors.
-
Ureters:
- The ureters are the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The ultrasound can visualize the ureters and detect any blockages or abnormalities.
-
Bladder:
- The bladder is examined for size, shape, and signs of abnormalities such as tumors or bladder stones.
-
Preparation:
- In many cases, no special preparation is required for a KUB ultrasound. However, it's advisable to follow any specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider or imaging facility.
-
Non-Invasive:
- KUB ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve radiation. It is considered safe and is often used as a first-line imaging tool for assessing the urinary system.
-
Complementary Tests:
- In some cases, a KUB ultrasound may be complemented by other imaging studies, such as a CT scan, to provide more detailed information.
KUB ultrasounds are valuable in diagnosing and monitoring a range of urinary system conditions. The results can help healthcare providers determine the appropriate course of treatment or further diagnostic testing if needed. If you are scheduled for a KUB ultrasound or have specific concerns about your urinary health, it's important to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Get In Touch
Tags
- Pasricha Clinic & Diagnostic Centre Rohini
- Pasricha Clinic & Diagnostic Centre Rohini Sector 13
- Dr. Aghosh Pasricha Diabetologist
- Dr. Aghosh Pasricha Consultant Physician
- Dr. Kamini Pasricha Consultant Radiologist
- Dr. Kamini Pasricha Ultrasonologist
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 13
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 13
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 13
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 13
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 13
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 13
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 13
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 13
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 13
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 13
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 13
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 13
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 13
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 13
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 13
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 13
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 13
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 13
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 13
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 13
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 13
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 13
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 13
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 13
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 13
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 13
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 13
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 13
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 13
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 13
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 13
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 13
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 13
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 14
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 14
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 14
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 14
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 14
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 14
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 14
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 14
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 14
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 14
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 14
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 14
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 14
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 14
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 14
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 14
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 14
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 14
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 14
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 14
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 14
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 14
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 14
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 14
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 14
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 14
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 14
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 14
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 14
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 14
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 14
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 14
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 14
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 15
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 15
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 15
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 15
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 15
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 15
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 15
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 15
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 15
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 15
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 15
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 15
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 15
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 15
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 15
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 15
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 15
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 15
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 15
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 15
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 15
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 15
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 15
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 15
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 15
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 15
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 15
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 15
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 15
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 15
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 15
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 15
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 15
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 11
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 11
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 11
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 11
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 11
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 11
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 11
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 11
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 11
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 11
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 11
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 11
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 11
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 11
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 11
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 11
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 11
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 11
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 11
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 11
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 11
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 11
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 11
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 11
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 11
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 11
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 11
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 11
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 11
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 11
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 11
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 11
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 11
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 16
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 16
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 16
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 16
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 16
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 16
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 16
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 16
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 16
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 16
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 16
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 16
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 16
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 16
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 16
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 16
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 16
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 16
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 16
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 16
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 16
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 16
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 16
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 16
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 16
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 16
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 16
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 16
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 16
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 16
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 16
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 16
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 16
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 9
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 9
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 9
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 9
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 9
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 9
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 9
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 9
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 9
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 9
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 9
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 9
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 9
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 9
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 9
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 9
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 9
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 9
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 9
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 9
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 9
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 9
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 9
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 9
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 9
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 9
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 9
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 9
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 9
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 9
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 9
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 9
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 9
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 7
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 7
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 7
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 7
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 7
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 7
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 7
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 7
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 7
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 7
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 7
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 7
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 7
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 7
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 7
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 7
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 7
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 7
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 7
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 7
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 7
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 7
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 7
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 7
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 7
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 7
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 7
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 7
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 7
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 7
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 7
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 7
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 7
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 6
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 6
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 6
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 6
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 6
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 6
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 6
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 6
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 6
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 6
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 6
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 6
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 6
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 6
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 6
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 6
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 6
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 6
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 6
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 6
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 6
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 6
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 6
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 6
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 6
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 6
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 6
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 6
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 6
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 6
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 6
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 6
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 6
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 5
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 5
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 5
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 5
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 5
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 5
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 5
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 5
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 5
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 5
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 5
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 5
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 5
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 5
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 5
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 5
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 5
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 5
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 5
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 5
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 5
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 5
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 5
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 5
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 5
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 5
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 5
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 5
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 5
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 5
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 5
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 5
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 5
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 17
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 17
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 17
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 17
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 17
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 17
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 17
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 17
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 17
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 17
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 17
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 17
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 17
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 17
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 17
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 17
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 17
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 17
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 17
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 17
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 17
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 17
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 17
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 17
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 17
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 17
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 17
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 17
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 17
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 17
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 17
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 17
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 17
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini Sector 18
- Best Clinic in Rohini Sector 18
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini Sector 18
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini Sector 18
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini Sector 18
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini Sector 18
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 18
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini Sector 18
- Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 18
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini Sector 18
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini Sector 18
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini Sector 18
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini Sector 18
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 18
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini Sector 18
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini Sector 18
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 18
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini Sector 18
- NT NB Scan in Rohini Sector 18
- Level II Scan in Rohini Sector 18
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini Sector 18
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 18
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini Sector 18
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini Sector 18
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini Sector 18
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini Sector 18
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini Sector 18
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 18
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini Sector 18
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini Sector 18
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 18
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini Sector 18
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini Sector 18
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Pitampura
- Best Clinic in Pitampura
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Pitampura
- Best Consultant Physician in Pitampura
- Best Diabetologist in Pitampura
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Pitampura
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Pitampura
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Pitampura
- Female Radiologist in Pitampura
- Best Female Radiologist in Pitampura
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Pitampura
- Best Ultrasonologist in Pitampura
- ECG Test Centre in Pitampura
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Pitampura
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Pitampura
- Follicular Monitoring in Pitampura
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Pitampura
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Pitampura
- NT NB Scan in Pitampura
- Level II Scan in Pitampura
- Color Doppler Test in Pitampura
- Whole Abdomen USG in Pitampura
- Lower Abdomen USG in Pitampura
- Upper Abdomen Test in Pitampura
- KUB Ultrasound in Pitampura
- Digital X Ray Centre in Pitampura
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Pitampura
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Pitampura
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Pitampura
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Pitampura
- Heart Problems Treatment in Pitampura
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Pitampura
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Pitampura
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rohini
- Best Clinic in Rohini
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rohini
- Best Consultant Physician in Rohini
- Best Diabetologist in Rohini
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rohini
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rohini
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rohini
- Female Radiologist in Rohini
- Best Female Radiologist in Rohini
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rohini
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rohini
- ECG Test Centre in Rohini
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rohini
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rohini
- Follicular Monitoring in Rohini
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rohini
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rohini
- NT NB Scan in Rohini
- Level II Scan in Rohini
- Color Doppler Test in Rohini
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rohini
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rohini
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rohini
- KUB Ultrasound in Rohini
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rohini
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rohini
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rohini
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rohini
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rohini
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rohini
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rohini
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rohini
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Prashant Vihar
- Best Clinic in Prashant Vihar
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Prashant Vihar
- Best Consultant Physician in Prashant Vihar
- Best Diabetologist in Prashant Vihar
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Prashant Vihar
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Prashant Vihar
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Prashant Vihar
- Female Radiologist in Prashant Vihar
- Best Female Radiologist in Prashant Vihar
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Prashant Vihar
- Best Ultrasonologist in Prashant Vihar
- ECG Test Centre in Prashant Vihar
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Prashant Vihar
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Prashant Vihar
- Follicular Monitoring in Prashant Vihar
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Prashant Vihar
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Prashant Vihar
- NT NB Scan in Prashant Vihar
- Level II Scan in Prashant Vihar
- Color Doppler Test in Prashant Vihar
- Whole Abdomen USG in Prashant Vihar
- Lower Abdomen USG in Prashant Vihar
- Upper Abdomen Test in Prashant Vihar
- KUB Ultrasound in Prashant Vihar
- Digital X Ray Centre in Prashant Vihar
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Prashant Vihar
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Prashant Vihar
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Prashant Vihar
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Prashant Vihar
- Heart Problems Treatment in Prashant Vihar
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Prashant Vihar
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Prashant Vihar
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Rithala
- Best Clinic in Rithala
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Rithala
- Best Consultant Physician in Rithala
- Best Diabetologist in Rithala
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Rithala
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Rithala
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Rithala
- Female Radiologist in Rithala
- Best Female Radiologist in Rithala
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Rithala
- Best Ultrasonologist in Rithala
- ECG Test Centre in Rithala
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Rithala
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Rithala
- Follicular Monitoring in Rithala
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Rithala
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Rithala
- NT NB Scan in Rithala
- Level II Scan in Rithala
- Color Doppler Test in Rithala
- Whole Abdomen USG in Rithala
- Lower Abdomen USG in Rithala
- Upper Abdomen Test in Rithala
- KUB Ultrasound in Rithala
- Digital X Ray Centre in Rithala
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Rithala
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Rithala
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Rithala
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Rithala
- Heart Problems Treatment in Rithala
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Rithala
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Rithala
- Best Diagnostic Centre in Shalimar Bagh
- Best Clinic in Shalimar Bagh
- Internal Medicine Specialist in Shalimar Bagh
- Best Consultant Physician in Shalimar Bagh
- Best Diabetologist in Shalimar Bagh
- Best Clinical Cardiologist in Shalimar Bagh
- Thyroid Treatment Specialist in Shalimar Bagh
- Chest Treatment Specialist in Shalimar Bagh
- Female Radiologist in Shalimar Bagh
- Best Female Radiologist in Shalimar Bagh
- Best Consultant Radiologist in Shalimar Bagh
- Best Ultrasonologist in Shalimar Bagh
- ECG Test Centre in Shalimar Bagh
- Soft Tissue Ultrasound in Shalimar Bagh
- Antral Follicle Count Test in Shalimar Bagh
- Follicular Monitoring in Shalimar Bagh
- TVS Ultrasound Centre in Shalimar Bagh
- Breast Ultrasound Centre in Shalimar Bagh
- NT NB Scan in Shalimar Bagh
- Level II Scan in Shalimar Bagh
- Color Doppler Test in Shalimar Bagh
- Whole Abdomen USG in Shalimar Bagh
- Lower Abdomen USG in Shalimar Bagh
- Upper Abdomen Test in Shalimar Bagh
- KUB Ultrasound in Shalimar Bagh
- Digital X Ray Centre in Shalimar Bagh
- Diabetes Management Specialist in Shalimar Bagh
- Infectious Disease Treatment in Shalimar Bagh
- Respiratory Disorders Treatment in Shalimar Bagh
- Gastro Disease Treatment in Shalimar Bagh
- Heart Problems Treatment in Shalimar Bagh
- Neuro Problems Treatment in Shalimar Bagh
- Miscellaneous Disorder Treatment in Shalimar Bagh
- show more
- show less





